Turing Machine
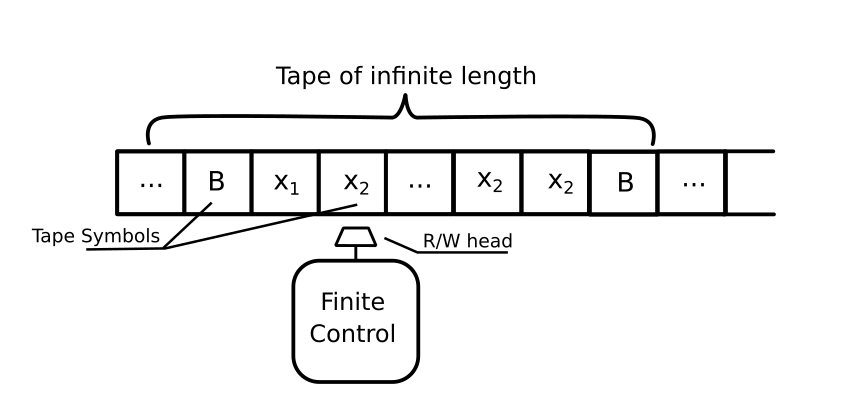
A hypothetical machine invented by Alan Turing in 1936, the Turing Machine has the ability to replicate any computer algoritihm, no matter its complexity. It is comprised of a read/write head, and an instruction set, though in its entirity it takes up a whole room. It was created during World War II so that England could intercept Germany's transmission and learn the German's plan to shorten the war by 2 years. This machine was revolutionary because it could compute any problem and solve any logic problems, making it far more power than any other computing machine at the time.